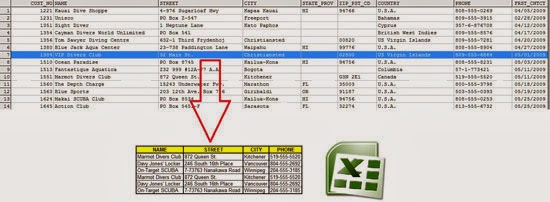
Introduction
Although her problem was related to Visual Basic 6.0 I sent her a quick solution using early binding. The next days I re-examined the code and I adjusted to VBA, converting it also to late binding. Since some people use DBF files, I thought that the developed VBA code might be useful for them. So, if you are interested in learning how to read DBF files from Excel, keep reading!
VBA code
Option Explicit
Sub ReadDBF()
'-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'This macro opens the Sample.dbf database, runs an SQL query (filtering all
'the country data from Canada) and copies the results back in the Excel sheet.
'The code uses late binding, so no reference to external library is required.
'Written by: Christos Samaras
'Date: 25/09/2013
'e-mail: [email protected]
'site: https://myengineeringworld.net/////
'-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'Declaring the necessary variables.
Dim con As Object
Dim rs As Object
Dim DBFFolder As String
Dim FileName As String
Dim sql As String
Dim myValues() As String
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
'Disable screen flickering.
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
'Specify the folder and the filename of the dbf file. If you use full path like
'C:UsersChristosDesktop be careful not to forget the backslash at the end.
DBFFolder = ThisWorkbook.Path & ""
FileName = "Sample.dbf"
On Error Resume Next
'Create the ADODB connection object.
Set con = CreateObject("ADODB.connection")
'Check if the object was created.
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Connection was not created!", vbCritical, "Connection error"
Exit Sub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
'Open the connection.
con.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & DBFFolder & ";Extended Properties=dBASE IV;"
'Create the SQL statement to read the file. Filter all the data from Canada.
'Note that the filename is used instead of the table name.
sql = "SELECT * FROM " & Left(FileName, (InStrRev(FileName, ".", -1, vbTextCompare) - 1)) & " WHERE COUNTRY='Canada'"
On Error Resume Next
'Create the ADODB recordset object.
Set rs = CreateObject("ADODB.recordset")
'Check if the object was created.
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Connection was not created!", vbCritical, "Connection error"
Exit Sub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
'Set thee cursor location.
rs.CursorLocation = 3 'adUseClient on early binding
rs.CursorType = 1 'adOpenKeyset on early binding
'Open the recordset.
rs.Open sql, con
'Redim the table that will contain the filtered data.
ReDim myValues(rs.RecordCount, 4)
'Loop through the recordset and pass the selected values to the array.
i = 1
If Not (rs.EOF And rs.BOF) Then
'Go to the first record.
rs.MoveFirst
Do Until rs.EOF = True
myValues(i, 1) = rs!Name
myValues(i, 2) = rs!Street
myValues(i, 3) = rs!City
myValues(i, 4) = rs!Phone
'Move to the next record.
rs.MoveNext
i = i + 1
Loop
Else
'Close the recordet and the connection.
rs.Close
con.Close
'Release the objects.
Set rs = Nothing
Set con = Nothing
'Enable the screen.
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
'In case of an empty recordset display an error.
MsgBox "There are no records in the recordset!", vbCritical, "No Records"
Exit Sub
End If
'Write the array in the sheet.
Sheet1.Activate
For i = 1 To UBound(myValues)
For j = 1 To 4
Cells(i + 1, j) = myValues(i, j)
Next j
Next i
'Close the recordet and the connection.
rs.Close
con.Close
'Release the objects.
Set rs = Nothing
Set con = Nothing
'Adust the columns width.
Columns("A:D").EntireColumn.AutoFit
'Enable the screen.
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
'Inform the user that the macro was executed successfully.
MsgBox "The values were read from recordset successfully!", vbInformation, "Done"
End Sub
Note that the above code was written for demonstration purposes. A similar approach can be applied also with Microsoft Access files. However, some adjustments in the VBA code need to be done first.
Download it from here
The zip file contains an Excel workbook that contains the VBA code presented above, as well as a sample DBF database. The workbook can be opened with Excel 2007 or newer.
Read also
Running Access Queries From Excel Using VBA



Hi,
Thank you for the suggestions.
A lot of code samples in this site are several years old.
If I find some time to re-work them, I will definitely write them differently.
Best Regards,
Christos
also, if Table name is longer that 8 chars, Tables could get not properly loaded if some of them has same 8 first chars on name.
That way you should get the TableName/FileName with the following code, and enclose TableName/FileName between brackets
I would either declare, so it can handle “Null” values:
Dim myValues() As Variant
You’re welcome, my friend!
Thank You Mr. Christos Samaras .