Introduction
We have seen in the past how to run Access queries from Excel, as well as how to export Access data to Excel. It’s time now to learn how to add records to an existing Access table. In the next paragraph, you will find a VBA code snippet used from Excel to add data into an existing Access table. The idea behind the code is the following:
- Create and open a connection to the Access database.
- Create and open a recordset that will contain the table data.
- Loop through Excel data and add them to the recordset (row by row).
- Update the recordset (row by row).
- Close both recordset and connection.
Before we dive into the VBA code, let’s see how to accomplish the same thing, but manually, shall we?
How to manually add records into Access table from Excel
The 6-step importing process can be done by using the Access wizard that was created for this reason.
Step 1: Open the Access database, select the “External Data” tab in the Ribbon, and in the group “Import & Link,” click the Excel button.
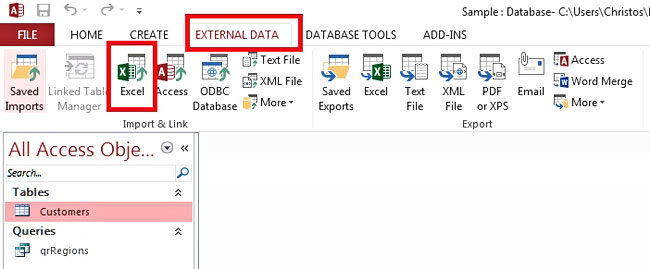
Step 2: Click the “Browse” button and find the spreadsheet file that contains the data to be imported. Click the “Append a copy of the records to the table” radio button, and from the dropdown, select the appropriate table (in this case, “Customers”). Then, click the “OK” button.
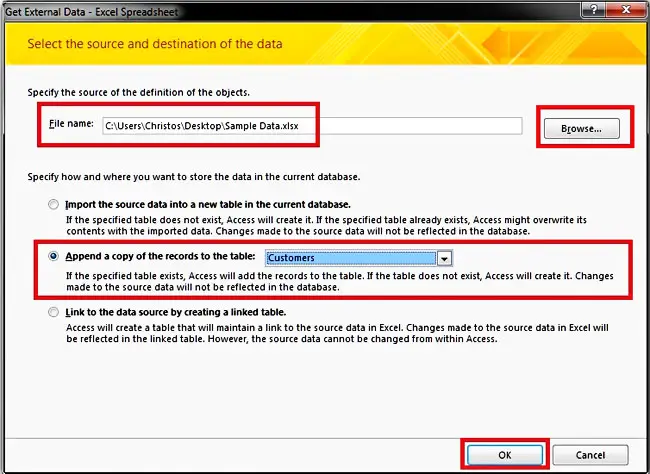
Step 3: If your spreadsheet contains multiple sheets, then you will have to click on the “Show Worksheets” radio button, select the appropriate sheet (here “Sheet1”) and click the “Next” button. Note that this form will not appear if the selected spreadsheet contains only a single worksheet.
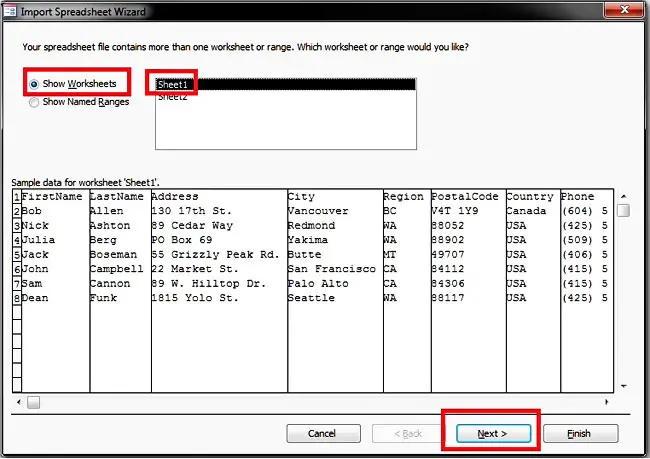
Step 4: If your headers are in the first row, the corresponding checkbox will already be checked on the next screen. Click the “Next” button.
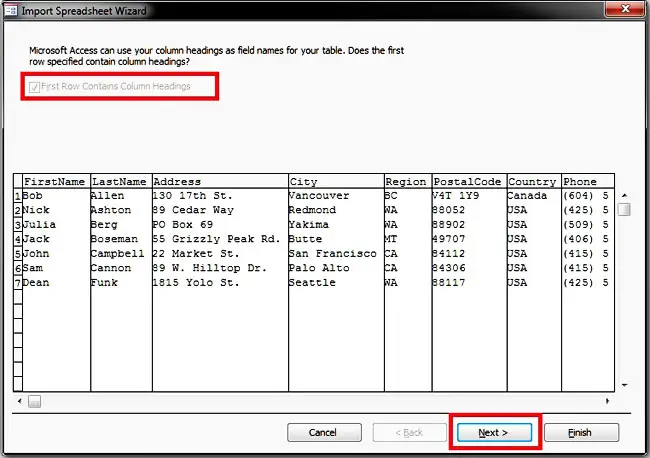
Step 5: In the next form of the wizard, check the “I would like a wizard to analyze my table after importing the data.” If you like, or you can click the “Finish” button.
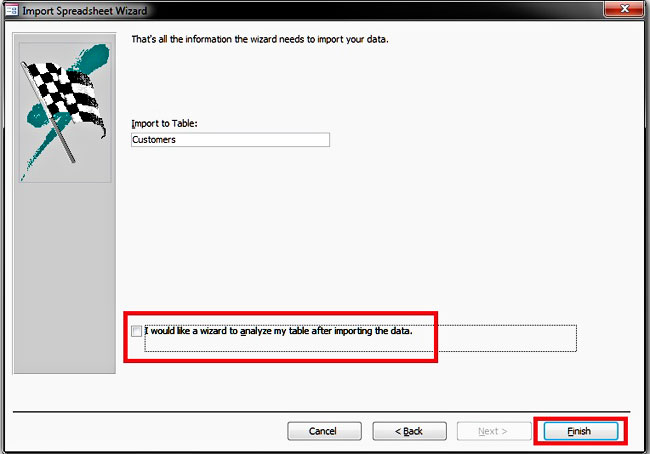
Step 6: In the latter case, the wizard’s final form will ask you if you want to save the import step. You can click the “Close” button.
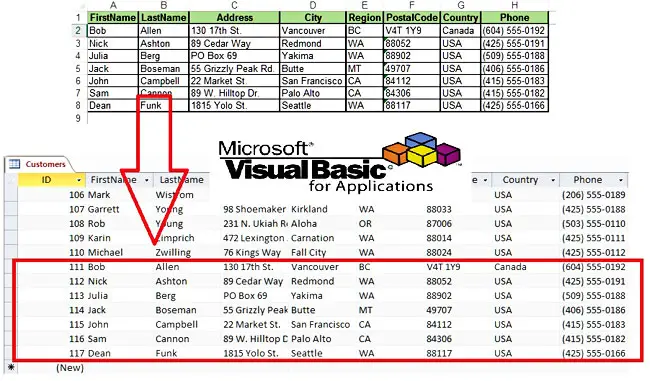
Congratulations! You just imported the Excel data into the Access table.
VBA code
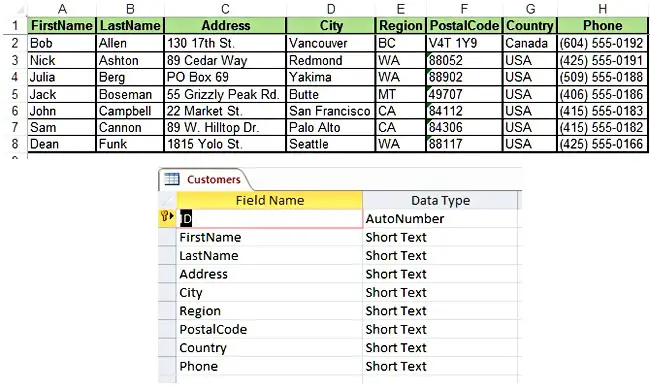
As the above image shows, two things should be carefully considered when using this VBA code:
- The Excel sheet headers should match the Access table ones (e.g., cell A1: FirstName, Access header: FirstName).
- The Excel sheet data should be of the same data type as the ones in the Access table (e.g., you cannot add a string value in an integer field).
Option Explicit
Sub AddRecordsIntoAccessTable()
'-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
'The macro opens the Sample.accdb database and adds the 7 rows from the sheet
'"Excel Data" in the "Customers" table of the database.
'The code uses late binding, so no reference to external library is required.
'Written By: Christos Samaras
'Date: 27/06/2020
'E-mail: [email protected]
'Site: https://myengineeringworld.net
'-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
'Declaring the necessary variables.
Dim accessFile As String
Dim accessTable As String
Dim sht As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim lastColumn As Integer
Dim con As Object
Dim rs As Object
Dim sql As String
Dim i As Long
Dim j As Integer
'Disable the screen flickering.
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
'Specify the file path of the accdb file. You can also use the full path of the file like this:
'AccessFile = "C:\Users\Christos\Desktop\Sample.accdb"
accessFile = ThisWorkbook.Path & "\" & "Sample.accdb"
'Ensure that the Access file exists.
If FileExists(accessFile) = False Then
MsgBox "The Access file doesn't exist!", vbCritical, "Invalid Access file path"
Exit Sub
End If
'Set the name of the table you want to add the data.
accessTable = "Customers"
'Set the worksheet that contains the data.
On Error Resume Next
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Excel Data")
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "The given worksheet does not exist!", vbExclamation, "Invalid Sheet Name"
Exit Sub
End If
Err.Clear
'Find the last row and last column in the given worksheet.
With sht
lastRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row
lastColumn = .Cells(1, .Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
End With
'Check if there are data in the worksheet.
If lastRow < 2 Or lastColumn < 1 Then
MsgBox "There are no data in the given worksheet!", vbCritical, "Empty Data"
Exit Sub
End If
'Create the ADODB connection object.
Set con = CreateObject("ADODB.connection")
'Check if the object was created.
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "The connection was not created!", vbCritical, "Connection Error"
Exit Sub
End If
Err.Clear
'Open the connection.
con.Open "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;Data Source=" & accessFile
'Create the SQL statement to retrieve the table data (the entire table).
sql = "SELECT * FROM " & accessTable
'Create the ADODB recordset object.
Set rs = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
'Check if the object was created.
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Set rs = Nothing
Set con = Nothing
MsgBox "The recordset was not created!", vbCritical, "Recordset Error"
Exit Sub
End If
Err.Clear
'Set the necessary recordset properties.
rs.CursorType = 1 'adOpenKeyset on early binding
rs.LockType = 3 'adLockOptimistic on early binding
'Open the recordset.
rs.Open sql, con
'Add the records from Excel to Access by looping through the rows and columns of the given worksheet.
'Here the headers are in the row 1 and they are identical to the Access table headers.
'This is the reason why, for example, there are no spaces in the headers of the sample worksheet.
For i = 2 To lastRow
rs.AddNew
For j = 1 To lastColumn
'This is how it will look like the first time (i = 2, j = 1):
'rs("FirstName") = "Bob"
rs(sht.Cells(1, j).Value) = sht.Cells(i, j).Value
Next j
rs.Update
Next i
'Close the recordet and the connection.
rs.Close
con.Close
'Release the objects.
Set rs = Nothing
Set con = Nothing
'Re-enable the screen.
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
'Inform the user that the macro was executed successfully.
MsgBox lastRow - 1 & " rows were successfully added into the '" & accessTable & "' table!", vbInformation, "Done"
End Sub
Function FileExists(FilePath As String) As Boolean
'--------------------------------------------------
'Checks if a file exists (using the Dir function).
'--------------------------------------------------
On Error Resume Next
If Len(FilePath) > 0 Then
If Not Dir(FilePath, vbDirectory) = vbNullString Then FileExists = True
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End Function The code uses the Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) library, but in late binding, so no external reference is required.
Downloads
The zip file contains an Excel workbook containing the VBA code presented above, a second workbook that can be used to import the data manually, as well as a sample Access database. The workbooks can be opened with Excel 2007 or newer.
Final thoughts
I know that the manual way (i.e., using the wizard) may seem easier than the VBA approach. Indeed, for cases where you want to add records from one table with “static” data, this is probably the preferable way to do it. However, if the spreadsheet data are the intermediate results of a longer calculating process, then the VBA approach, adjusted accordingly, will probably offer more flexibility. The final decision is up to you!
Read also
Running Access Queries From Excel Using VBA
Export A Large Access Table/Query To Excel


Hi, Bradley,
Did you try the sample zip file with the sample database or a different file/database?
If you are using a different file, then bear in mind that the VBA code, as it is, does not check the validity of the field names.
So, check if the headers in the Excel sheet are the same with the headers of the Access table.
Best Regards,
Christos
Hi Cristos,
great post. I have tried to use this and the code seems to work, and tells me that the record was added to my target table. however, the data actually isnt in the table.
Hi, Xin, and thank you for your kind words.
Working with attachments is easier with DAO than with ADO.
Here are a few examples from Microsoft.
Best Regards,
Christos
Hi, Christos, Thanks a lot, this article helps me a lot. Just another question related with this topic, your article showed how to import excel data to access database. In my case, there will be a or several scan file(s) corresponding to each piece of data. My question is how to upload these attachments to the access database together with the excel data.
Hello again Christos, I found the solution for my problem. I’ve add:
“`
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
On Error GoTo 0
“`
Before looping through the rows and columns of the worksheet.
Then I’ve got new problems, how do I do if:
1. Update access table if the record is duplicate.
2. Add new record to access table if the record is not duplicate.
Hi, Jessica and thank you for your kind words.
Without seeing your settings (spreadsheet/access), it is hard to tell what is going wrong.
However, I have the following question for you:
If you download the sample files and run the code, are the records added to the sample database?
If this is not happening, then there might be a generic issue on your computer (e.g. a connection problem – OLEDB provider).
If the sample files are working, then in your case, there might be something wrong either with your spreadsheet or the database (e.g. a data mismatch).
Try the sample files and let me know about the results.
Best Regards,
Christos
Hi Christos, your article help me so much. I thank you for that. However I found this difficulties that I’d been used the code and it says that the records has been successfully stored to the table in access database. But then when I checked in the table, there are no records that I’ve been added. Could you identify where’s the wrong step of mine?
I just sent you an email for the other question.
Hi Christos
Thank you very much for your quick reply, I will be looking forward to your new articles.
However I was preparing an email with another question, that if you find it interesting or are in the spirit of the articles you are going to do, you can also incorporate the respective clarification.
Thank you very much for your clarification
Jorge
Hi, Jorge,
First of all, thank you for your kind words.
Regarding your question, the answer depends on the uniqueness of the data and how you will check that uniqueness.
Since this might sound vague, let me give you an example:
If you want to import typical customer information (e.g. Name, Last Name, Address, etc.), you can probably check if there is already a customer in the Access table with the same Name, Last Name (and even Address) with the one you want to import.
In other words, the uniqueness check strongly depends on the available data.
I am planning to publish an article on how to update existing data in Access from Excel.
The article will contain some practical examples of uniqueness checks.
I will even add an example that will show how to update or import the data (what you asked for) for demonstration purposes.
So, stay tuned!
Best Regards,
Christos
Hi Christos
This is an excellent and useful post, at all levels.
However I was left with a small / big doubt, which is the following: imagine that in Excel data, there are data that already exist in Access, how do I update the data in these cases and, when not in Access, add the new ones ?
Thanks