Introduction
Almost 4.5 years have passed since the last post that I published dealing with AutoCAD and Excel cross-application development. Well, that’s quite a long time, don’t you think? Anyway, we have already learned how to draw several objects in AutoCAD from Excel (e.g. polylines, circles, and points), as well as how to add text and blocks in a drawing. But, how about dimensions? Is it possible to add dimensions in an AutoCAD drawing from Excel? Of course, it is!
The proposed solution is based on the AddDimAligned method of AutoCAD, which creates an aligned dimension to the specified document. According to AutoCAD VBA help, the structure of AddDimAligned method is the following:
RetVal = object.AddDimAligned(ExtLine1Point, ExtLine2Point, TextPosition)
RetVal: The newly created aligned dimension.
Object: Block, ModelSpace and PaperSpace. The objects this method applies to.
ExtLine1Point: Variant (three-element array of doubles). The 3D WCS coordinates specifying the first endpoint of the extension line.
ExtLine2Point: Variant (three-element array of doubles). The 3D WCS coordinates specifying the second endpoint of the extension line.
TextPosition: Variant (three-element array of doubles). The 3D WCS coordinates specifying the text position.
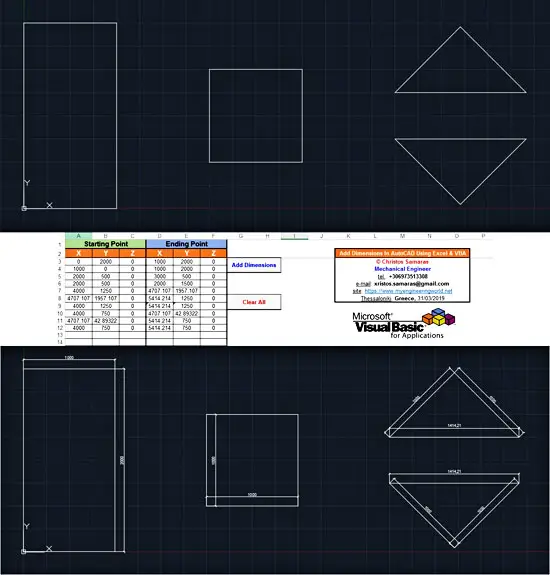
The sample workbook that you will find in the Downloads section below requires two main parameters: the coordinates of the starting point (ExtLine1Point) and the ending point (ExtLine2Point). The position of the displayed text (TextPosition) is automatically calculated in the middle of the two points.
VBA code for adding dimensions to AutoCAD from Excel
The code is actually a loop; most of the code is used to initialize the AutoCAD application object, as well as to open the sample drawing or to create a new one. Inside the code, you will find several formatting options, which you can customize according to your needs. Moreover, the dimOffset variable is used for adding an extra space between the dimension line and the object that is measured.
Option Explicit
Sub AddDimensions()
'-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'The macro adds the dimensions that exist in the sheet named "Dimensions" to the opened or to a new AutoCAD drawing.
'It uses the AutoCAD AddDimAligned method to add the dimensions.
'The code uses late binding, so no reference to external AutoCAD (type) library is required.
'It goes without saying that AutoCAD, as well as VBA in AutoCAD, must be installed at your computer before running this code.
'Written By: Christos Samaras
'Date: 14/03/2019
'Last Updated: 08/04/2019
'E-mail: [email protected]
'Site: https://myengineeringworld.net
'-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'Declaring the necessary variables.
Dim acadApp As Object
Dim acadDoc As Object
Dim acadDimAligned As Object
Dim startingPoint(2) As Double
Dim endingPoint(2) As Double
Dim textLocation(2) As Double
Dim dimOffset As Double
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
'This is the vertical distance between the objected measured and the dimension line.
'You can adjust it according to your needs.
dimOffset = 100
'Activate the dimensions sheet and find the last row.
With Sheets("Dimensions")
.Activate
lastRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
End With
'Check if there are coordinates for at least one dimension.
If lastRow < 3 Then
MsgBox "There are no coordinates in the sheet!", vbCritical, "Coordinates Error"
Exit Sub
End If
'Check if AutoCAD application is open. If is not opened create a new instance and make it visible.
On Error Resume Next
Set acadApp = GetObject(, "AutoCAD.Application")
If acadApp Is Nothing Then
Set acadApp = CreateObject("AutoCAD.Application")
acadApp.Visible = True
End If
'Check (again) if there is an AutoCAD object.
If acadApp Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Sorry, it was impossible to start AutoCAD!", vbCritical, "AutoCAD Error"
Exit Sub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
'Try to open the sample drawing.
On Error Resume Next
Set acadDoc = acadApp.Documents.Open(ThisWorkbook.Path & "\" & "Sample Drawing.dwg")
'If the sample file cannot be opened, create a new drawing.
If acadDoc Is Nothing Then
Set acadDoc = acadApp.Documents.Add
End If
On Error GoTo 0
'Check if the active space is paper space and change it to model space.
If acadDoc.ActiveSpace = 0 Then '0 = acPaperSpace in early binding
acadDoc.ActiveSpace = 1 '1 = acModelSpace in early binding
End If
On Error Resume Next
'Loop through all the rows of the sheet and add the corresponding dimensions in the drawing.
With Sheets("Dimensions")
For i = 3 To lastRow
'Set the starting point.
startingPoint(0) = .Range("A" & i).Value
startingPoint(1) = .Range("B" & i).Value
startingPoint(2) = .Range("C" & i).Value
'Set the ending point.
endingPoint(0) = .Range("D" & i).Value
endingPoint(1) = .Range("E" & i).Value
endingPoint(2) = .Range("F" & i).Value
'Calculate the text location point.
If startingPoint(1) = endingPoint(1) Then
'Horizontal line.
textLocation(0) = (startingPoint(0) + endingPoint(0)) / 2
textLocation(1) = startingPoint(1) + dimOffset
textLocation(2) = startingPoint(2)
ElseIf startingPoint(0) = endingPoint(0) Then
'Vertical line.
textLocation(0) = startingPoint(0) + dimOffset
textLocation(1) = (startingPoint(1) + endingPoint(1)) / 2
textLocation(2) = startingPoint(2)
Else
'Any other line.
If startingPoint(1) > endingPoint(1) Then
textLocation(0) = (startingPoint(0) + endingPoint(0)) / 2 + dimOffset
textLocation(1) = (startingPoint(1) + endingPoint(1)) / 2
textLocation(2) = startingPoint(2)
Else
textLocation(0) = (startingPoint(0) + endingPoint(0)) / 2 - dimOffset
textLocation(1) = (startingPoint(1) + endingPoint(1)) / 2
textLocation(2) = startingPoint(2)
End If
End If
'Add the dimension in the drawing.
Set acadDimAligned = acadDoc.ModelSpace.AddDimAligned(startingPoint, endingPoint, textLocation)
'Format the dimension object according to your needs.
With acadDimAligned
.TextHeight = 30
.TextGap = 10 'The distance of the dimension text from the dimension line.
.Arrowhead1Type = 5 'acArrowOblique in early binding
.Arrowhead2Type = 5 'For the standard dimension arrow put 0 here.
.ArrowheadSize = 20
.ExtensionLineExtend = 10 'The amount to extend the extension line beyond the dimension line.
End With
'Reset the arrays.
Erase startingPoint
Erase endingPoint
Erase textLocation
Next i
End With
'Zoom in to the drawing area.
acadApp.ZoomExtents
'Release the objects.
Set acadDimAligned = Nothing
Set acadDoc = Nothing
Set acadApp = Nothing
'Inform the user about the process.
MsgBox "The dimensions were successfully added in the drawing!", vbInformation, "Finished"
End Sub Note that if you have AutoCAD 2010 or a more recent version, you will have to download and install the VBA module, otherwise the code will fail. Just navigate to Autodesk‘s website and download the appropriate version.
Demonstration video
The short video below demonstrates the result of the above VBA code (10 dimensions are added in the drawing).
Downloads
The zip file contains an Excel workbook along with a sample drawing that can be used to test the VBA code. The workbook can be opened with Excel 2007 or newer. Please enable macros before using it.
Read also
Send AutoCAD Commands From Excel & VBA
Drawing Points In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Drawing Circles In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Add Text In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Send AutoCAD Commands From Excel & VBA


It’s Lisp in AutoCAD.
More info here:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lisp_(programming_language)
https://knowledge.autodesk.com/support/autocad/learn-explore/caas/sfdcarticles/sfdcarticles/Automatically-load-AutoLISP-routines.html
what is this command? what is language?
(defun numeric()
(setq scfc 111189000.0)
(textscr)
(princ “nMetric Scale
=============
(2000000) 1 : 2000000
(1000000) 1 : 1000000
(500000) 1 : 500000
(250000) 1 : 250000
(100000) 1 : 100000
(1) Full”)
(setq DRSC (GETREAL “nEnter Scale Number :”))
(setq width (getreal “nEnter Format width :”))
(setq height (getreal “nEnter Format height :”))
(setq paper_width (*(/ drsc scfc) width))
(setq paper_height(*(/ drsc scfc) height))
(setq plotscale (/ scfc drsc))
(setq FROM(GETPOINT “nPick First Corner :”))
(setq TO (strcat “@” (rtos paper_width 2 5) “,” (rtos paper_height 2 5)))
;*****************autocad command
(command “rectang” from to)
;********************************
(setq paper_width(strcat “Paper Width : ” (rtos PAPER_WIDTH 2 5)))
(setq paper_height(strcat “Paper Height : ” (rtos PAPER_HEIGHT 2 5)))
(setq plotscale(strcat “Plot Scale : ” (rtos plotscale 2 5)))
(textscr)
(PRINT paper_width)
(PRINT PAPER_HEIGHT)
(PRINT PLOTSCALE)
(print)
(print “This program create & design by Barju Ristiyanto”)
(PRINT)
)